In this article, you will learn: why varicose veins of the pelvis is considered a disease and not a variant of varicose veins of the legs; to whom this disease can occur and why. One of the manifestations and the diagnosis of this pathology, as treated properly, the chances of a cure.

Varicose veins of the pelvis is the weakening of the internal walls or external venous of vessels of the pelvic area, which leads to an excessive increase of its diameter. Esophageal varices modified from vienna are not able to ensure the reflux of the blood from the organs of the pelvis, which leads to the stagnation and the total destruction of the vascular wall. As a result of the violation of the structure and the female sexual function in the system.
The initial stages of the disease cause only a little discomfort in the area of the external genitalia and on the lower part of the abdomen. Women with running forms of pelvic varicose veins tormented of the strong pains of various diseases, gynaecological, sterile, they have a cosmetic defect in the form of a convoluted advanced venous of the nodes in the crotch area, sex, of the labia or at the entrance of the vagina.
The disease can be completely cured, but to prevent the recurrence of the necessary warranty for the life of the prevention. Dealing with this problem, next vascular, surgeons, obstetricians-gynecologists.
Varicose veins of the pelvis in men as in women, it is not. But this disease – varicocele. The mechanisms of onset and the manifestations are similar to those of being, when pelvic varicose veins. Varicose veins occurs in the left testicle and on the progress of the seeds of the umbilical cord by the fact that on the left side of vienna egg of the stagnant blood. It again is launched from the left renal vein, which empties vienna.
The essence of the pathology, in the extent of how serious
The Exterior and interior of women in the sex organs well krovosnabjaemah. To ensure that there is a reflux of the blood is required a strong network of venous vessels. Therefore, the venous system of the pelvis in women is well developed. Each vienna has a solid wall, is provided with valves, is close to pass the veins. All of this is consistent functioning of the venous network of the pelvic area, which collects the blood from the crotch, outside of the reproductive organs (vulva, vagina), special structures (ovaries, uterus), and carries at its lower Polow vienna.
Esophageal varices modified veins of the pelvis are different from the healthy, which are:
- Expanded diameter;
- Full of blood;
- Excessively convoluted;
- Have protuberances as nodes;
- Flabby and weak.
The pelvis of the affected vein by varicose veins, can collect the blood of the exterior genitalia and other organisms, but they are not usually able to carry more of the great vessels (hollow vein). This causes the stagnant blood in the pelvis, and penetrating through the wall of the vein, affects the tissues, which must reflow. Become swollen, inflamed and lose their functions.
But the thing that most varicose veins of the pelvis danger:
- The various violations of the ovaries.
- Uterine bleeding, and different disorders;
- The sterility, and the threat of interruption of pregnancy, and the impossibility of natural birth;
- Formation of blood clots in the lumen of the esophageal varices modified the veins, which represents a threat outside the area of education and migration in the heart and the vessels of the lungs. It is the most dangerous thing complication that threatens the life – the pulmonary embolism (ep).
The causes of the
Mainly varicose veins of the pelvis is that of the woman sexually mature:
- Before 20 years of age – 20%;
- 20 to 30 years – 30%
- 30 – 45 years – 50%
Mechanisms of veins of the degeneration of the venous system of the pelvis:
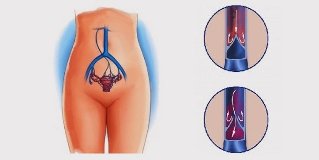
- (80%). They are the largest thematic veins that collect blood from the uterus and the ovaries, and are directly in the hollow of the right) or kidney (left) of vienna. If they are breakage has occurred, this avoids the venous reflux.
- Uniform weakening or destruction of the vein wall, all the veins of the pelvis – all of them at the same time expand and are not able to contract to push the blood in the biggest lie of the departments.
- The return of the blood from a deep vein in the hip in the sexual activity and a vein, collecting the blood from the perineum and genital organs external, prevents the reflux. As a result of the pressure increases, and the trunk and all tributaries esophageal varices are expanded.
The direct causes of the onset of these mechanisms may be:
- Innate weakness or dysplasia (underdevelopment) of the venous wall and valves.
- Hormonal alignment in the female body (puberty, pregnancy, menopause, diseases of the ovaries).
- Frequent inflammatory processes, endometriosis, operation, adhesive process in the pelvis.
- Transferred thrombosis and thrombophlebitis of the veins of the pelvis.
- Heavy-duty work.
- Long stay in the position of lying or sitting position.
- The excess of weight.
- The pregnancy and childbirth.
- Regulate the interruption of sexual relations over many years, especially in the absence of orgasm.
- The curves of the uterus later or the opposite.
- Tumors of the pelvis.
- When the uterus.
The degree of varicose veins – classification
For anatomical reasons (prevalence) varicose veins of the pelvis are divided into three types:
- Other venous hyperemia in the pelvis;
- Perineal varicose veins, etc.;
- Co-infections of the way.
To reflect the character of pathological changes of the disease are divided into three grades:
- The first – dilation of the vessels of any organ plexus of the pelvis does not exceed a diameter of 0.5 cm, overly convoluted.
- The second, the diameter of the veins increases up to 1 cm, distributed processing, not only in the plexus of organs(uterinoel, ovaries), but around them (okolomatocnah fiber).
- The third – of the extension (ectasia) of more than 1 cm, which affects all the vessels – intraorganic, around the organs, and the trunk (trunk ovary of vienna).
The higher the grade of the disease, the worse extended of vienna and heavier than the stagnation of blood in the pelvis.
The characteristic symptoms
Women with varicosities of the veins of the pelvis point to:
- Permanent or recurrent abdominal pain, the increase in the afternoon or after the loads mainly during the second half of the cycle (closer to months). With 3 degrees of pain can be very serious.
- Itching, burning, swelling and cyanosis of the genital organs.
- Painful menstruation and sexual intercourse.
- Abundant menstruation and uterine bleeding, irregular cycle.
- The inability to get pregnant.
- The lesions most convoluted of vienna in the area of the crotch and the lips.
- Frequent painful urination.
- Expressed manifestations of premenstrual syndrome.

The diagnosis
To confirm the diagnosis pass:
- The ultrasound through the abdomen and through the vagina (transvaginally) with the use of special sensors – Doppler, and duplex treatment of the veins of the pelvis. The easiest and more informative method.
- The phlebography – injected into ovary vienna.
- Computed tomography with enhancement.
- The diagnostic laparoscopy.
Methods of treatment
Varicose veins of the pelvis, along cure vascular surgeons midwife-gynecologists. According to the modern conceptions of treatment is composed of the following destinations:
- The normalization of the image of the life;
- Curator of the medication;
- Compression and other treatment;
- The surgical treatment.
Cure varicose veins of the pelvis. For this reason, professionals constitute a plan of treatment, the sick, women should always follow prevention and treatment recommendations.
1. The normalization of the image of the life
Given that the wrong image of life is a condition and the immediate cause of varicose veins, surgery of the veins of the pelvis, its standardisation will help to cure:
- Eliminate the prolonged stay in a standing position or sitting position (more than 2-3 hours non-stop).
- Do not lift heavy objects and discarding of hard physical work.
- During the day, do download the gymnastics for the pelvic (exercises berezka, bike) or simply relax for 10-15 minutes with the lifted above the level of the body of the pelvis.
- Reduce the weight in case of obesity).
- Do not take a hot bath, replace it by a contrast showers.
- Forget about alcohol and tobacco.
2. Medical therapy
Treatment of varicose veins, surgery of the pelvis veins of any degree, is not possible without drug support. The first measure is the main drug-like activity, in the second and third complements the comprehensive treatment.
Using these medications:
- Special medications reinforce venous vessels.
- Anticoagulant – dilute the blood, to facilitate the progress of the vessels.
- Drugs that improve the microcirculation.
For more groups of drugs are administered subject to the availability of deviations in the body:
- Drugs women of the sex hormones (when dishormonal violations).
- Analgesic and anti-inflammatory.
- Medicines to stop blood styptic medicines for the treatment of fallopian bleeding.
3. Compression therapy
One of the effective means in the treatment of varicose veins in the genital area and the perineum is the compression of the exposure. The principle of this method is equivalent to that of elastic bandages for varicose veins of the legs. Compression (compression) superficial veins from the outside contributes to their pouring out of the blood. Create an effect so special able to of tights or compression shorts therapeutic knitwear. You can buy them in pharmacies, shops, meeting rooms for the healthcare products individually, adapting the size and the compression force.
Sclerotherapy – puncture esophageal varices extension of the vein with the introduction into the lumen of the special drugs that are causing the paste. This treatment is performed in the exterior (subcutaneous) pelvic varicose veins without the need for hospitalization in the hospital. Internal of vienna can also be treated, but this procedure is technically more complex and goes under the knife.
4. The surgical treatment
Varicose veins of the pelvis it is better to treat in a manner operative to:
- 2-3 degrees of the disease;
- The rapid progression of the disease;
- The planning of the pregnancy;
- Clear syndrome painful;
- Permanent bleeding, uterine and other gynecological disorders.
The main types of operations to the pelvic varicose veins:
- Laparoscopic – special operation through the punctures in the belly. Made the bandage, the intersection or the removal of ovary vienna. Be it therefore resolved the return of the blood from it.
- The removal of the esophageal varices dilated veins through small punctures or cuts in the skin, are deleted, modified for subcutaneous, vienna, tied up outside, gender-vienna at the confluence of the vessels.
- Gynecologic surgery – the removal of tumors, removal of bends of the uterus.
Prognosis
If you do not heal the esophageal varices varicose veins in the pelvis, with time, more are expanded (95%), threat with dangerous complications. The rest of the 5% of women with subcutaneous varicose veins crotch 1-2 as they originated after the birth, the pathology does not increase, but that never would disappear.
If the disease is treated, you can achieve a full recovery (between 10% and 50%, depending on the degree), or the significant improvement of the state (45-50%), especially in the case of the combination of surgical techniques with conservative. But, in any case, after a comprehensive treatment, should have a warranty for the life of the prevention, which consists in the implementation of the recommendations of style of life, regular medication or compression support of the weak veins.






































